Figure 10
Download original image
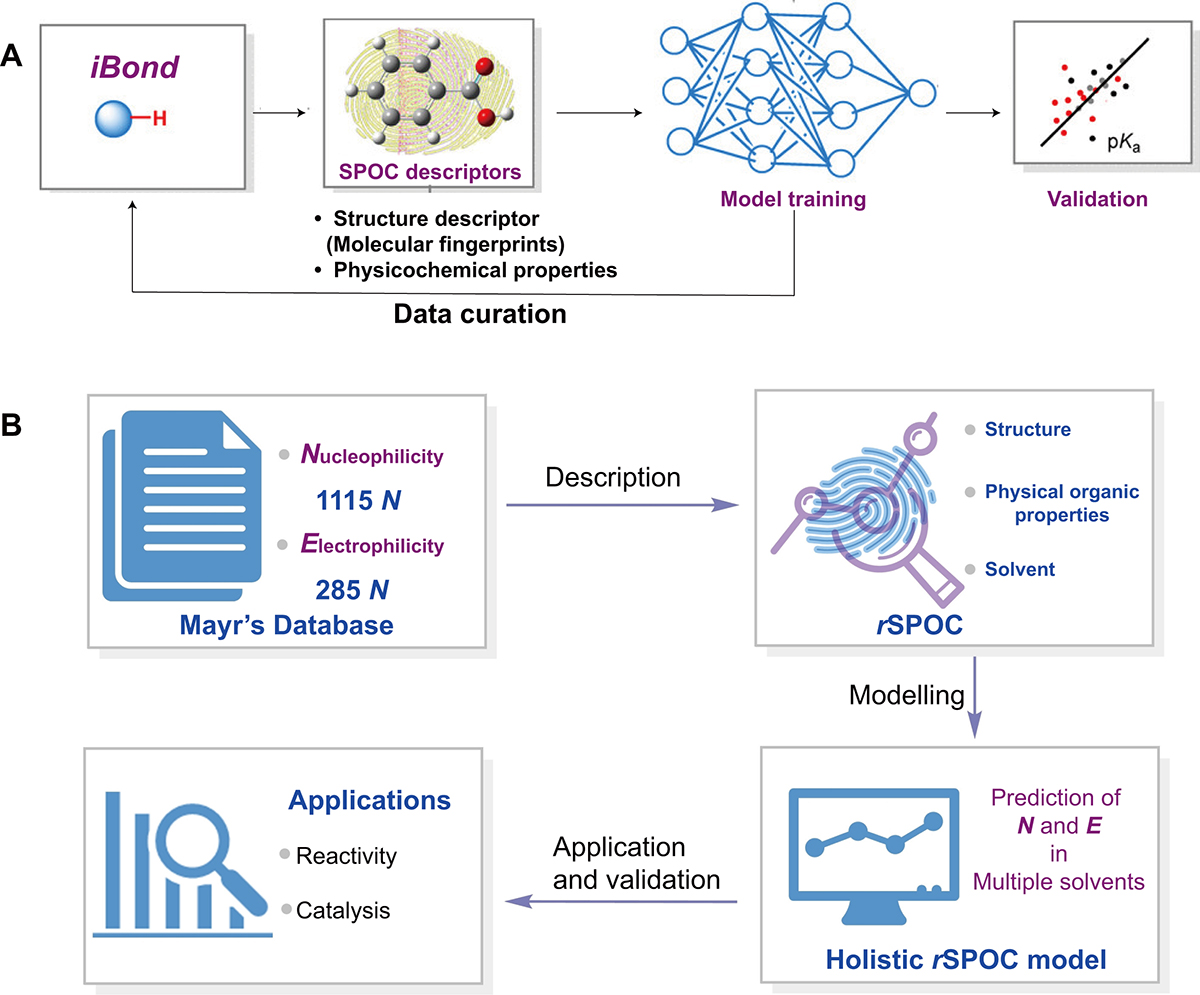
Data-driven reactivity predictions. (A) An advanced model has been engineered for predicting pKa values, leveraging the ibond database which encompasses data from 39 distinct solvents [79]. Copyright©2020, John Wiley and Sons. The machine-learning-driven model employs SPOC to capture the molecular electronic and structural features. Training using either a neural network or the XGBoost algorithm has resulted in its remarkable predictive prowess, evidenced by a minimum mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.87 pKa units. (B) A broad-scale predictive model, developed using machine learning techniques, has been introduced [81]. Copyright©2023, John Wiley and Sons. This innovative molecular representation, designated as rSPOC, amalgamates structural, physicochemical, and solvent-related elements. The model’s dataset incorporates 1115 nucleophiles, 285 electrophiles, and 22 solvents, thereby establishing it as the most expansive resource for reactivity prediction currently in existence.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.

